Ford Escape: Front Drive Halfshafts / Diagnosis and Testing - Front Drive Halfshafts
Preliminary Inspection
-
Visually inspect the CV joints, housing, boots, and clamps for obvious signs of mechanical damage.
-
If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is
found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to the next
step
-
If the cause is not visually evident, verify the symptom and REFER to Symptom Chart: NVH.
Symptom Chart(s)
Diagnostics in this manual assume a certain skill level and knowledge of Ford-specific diagnostic practices.
REFER to: Diagnostic Methods (100-00 General Information, Description and Operation).
Symptom Chart: NVH
Symptom Chart
| Condition | Actions |
|---|---|
| Axle howling or whine – front or rear axle | GO to Pinpoint Test A |
| Driveline clunk - loud clunk when shifting from REVERSE to DRIVE | GO to Pinpoint Test B |
| Driveline clunk (Front Wheel Drive (FWD) vehicles) — occurs during acceleration or from cruise to coast/deceleration | GO to Pinpoint Test C |
| Driveline clunk — occurs as the vehicle starts to move forward following a stop | GO to Pinpoint Test D |
| Clicking, popping or grinding - occurs while the vehicle is turning | GO to Pinpoint Test E |
| Grunting — normally associated with a shudder experienced during acceleration from a complete stop | GO to Pinpoint Test F |
| Driveline vibration - occurs at cruising speeds | GO to Pinpoint Test G |
Pinpoint Tests
 PINPOINT TEST A: AXLE HOWLING OR WHINE – FRONT OR REAR AXLE
PINPOINT TEST A: AXLE HOWLING OR WHINE – FRONT OR REAR AXLE |
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions Halfshafts transmit rotary motion through constant velocity joints in a uniform manner. The outer CV joints use balls, have no length compensation and engage in the wheel hubs. The intermediate shaft (right side) is correctly positioned and secured in the differential by the intermediate shaft center bearing. The left CV joint is locked in the differential by a snap-ring. Possible Sources
|
||||
| A1 INSPECT WHEEL HUB BEARINGS | ||||
Was any wheel hub bearing play or damage found?
|
 PINPOINT TEST B: DRIVELINE CLUNK- LOUD CLUNK WHEN SHIFTING FROM REVERSE TO DRIVE
PINPOINT TEST B: DRIVELINE CLUNK- LOUD CLUNK WHEN SHIFTING FROM REVERSE TO DRIVE|
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions Halfshafts transmit rotary motion through constant velocity joints in a uniform manner. The outer CV joints use balls, have no length compensation and engage in the wheel hubs. The intermediate shaft (right side) is correctly positioned and secured in the differential by the intermediate shaft center bearing. The left CV joint is locked in the differential by a snap-ring. Possible Sources
|
||||
| B1 CHECK THE HUB NUT TORQUE | ||||
Is the hub nut loose?
|
||||
| B2 CHECK THE TORQUE ON SUSPENSION AND STEERING SYSTEM FASTENERS | ||||
Is the any of the suspension and steering fastener loose?
|
||||
| B3 CHECK THE CONSTANT VELOCITY (CV) BOOTS AND JOINTS FOR WEAR OR DAMAGE | ||||
Was damage found?
|
 PINPOINT
TEST C: DRIVELINE CLUNK (FRONT WHEEL DRIVE (FWD) VEHICLES) — OCCURS
DURING ACCELERATION OR FROM CRUISE TO COAST/DECELERATION
PINPOINT
TEST C: DRIVELINE CLUNK (FRONT WHEEL DRIVE (FWD) VEHICLES) — OCCURS
DURING ACCELERATION OR FROM CRUISE TO COAST/DECELERATION |
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions Halfshafts transmit rotary motion through constant velocity joints in a uniform manner. The outer CV joints use balls, have no length compensation and engage in the wheel hubs. The intermediate shaft (right side) is correctly positioned and secured in the differential by the intermediate shaft center bearing. The left CV joint is locked in the differential by a snap-ring. Possible Sources
|
||||
| C1 CHECK THE HUB NUT TORQUE | ||||
Is the hub nut loose?
|
||||
| C2 CHECK THE TORQUE ON SUSPENSION AND STEERING SYSTEM FASTENERS | ||||
Is the any of the suspension and steering fastener loose?
|
||||
| C3 CHECK THE CONSTANT VELOCITY (CV) BOOTS AND JOINTS FOR WEAR OR DAMAGE | ||||
Was damage found?
|
 PINPOINT TEST D: DRIVELINE CLUNK — OCCURS AS THE VEHICLE STARTS TO MOVE FORWARD FOLLOWING A STOP
PINPOINT TEST D: DRIVELINE CLUNK — OCCURS AS THE VEHICLE STARTS TO MOVE FORWARD FOLLOWING A STOP |
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions Halfshafts transmit rotary motion through constant velocity joints in a uniform manner. The outer CV joints use balls, have no length compensation and engage in the wheel hubs. The intermediate shaft (right side) is correctly positioned and secured in the differential by the intermediate shaft center bearing. The left CV joint is locked in the differential by a snap-ring. Possible Sources
|
||||
| D1 CHECK FOR LOOSE HUB NUT | ||||
Are any hub nuts loose?
|
||||
| D2 CHECK THE TORQUE ON SUSPENSION AND STEERING SYSTEM FASTENERS | ||||
Is the any of the suspension and steering fastener loose?
|
 PINPOINT TEST E: CLICKING, POPPING OR GRINDING - OCCURS WHILE THE VEHICLE IS TURNING
PINPOINT TEST E: CLICKING, POPPING OR GRINDING - OCCURS WHILE THE VEHICLE IS TURNING |
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions Halfshafts transmit rotary motion through constant velocity joints in a uniform manner. The outer CV joints use balls, have no length compensation and engage in the wheel hubs. The intermediate shaft (right side) is correctly positioned and secured in the differential by the intermediate shaft center bearing. The left CV joint is locked in the differential by a snap-ring. Possible Sources
|
||||
| E1 CHECK THE CONSTANT VELOCITY (CV) BOOTS AND JOINTS FOR WEAR OR DAMAGE | ||||
Was wear or damage found?
|
||||
| E2 CHECK THE HALFSHAFTS FOR CONTACT WITH ANOTHER COMPONENT | ||||
Is there contact between other components with the halfshaft?
|
||||
| E3 INSPECT THE HALFSHAFT OR HALFSHAFT CIRCLIP | ||||
Was any damage found?
|
 PINPOINT TEST F: GRUNTING — NORMALLY ASSOCIATED WITH A SHUDDER EXPERIENCED DURING ACCELERATION FROM A COMPLETE STOP
PINPOINT TEST F: GRUNTING — NORMALLY ASSOCIATED WITH A SHUDDER EXPERIENCED DURING ACCELERATION FROM A COMPLETE STOP |
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions Halfshafts transmit rotary motion through constant velocity joints in a uniform manner. The outer CV joints use balls, have no length compensation and engage in the wheel hubs. The intermediate shaft (right side) is correctly positioned and secured in the differential by the intermediate shaft center bearing. The left CV joint is locked in the differential by a snap-ring. Possible Sources
|
||||
| F1 CHECK THE OUTER CONSTANT VELOCITY (CV) JOINT FOR CORRECT SEATING INTO THE HUB | ||||
Is the outer Constant Velocity (CV) joint seated correctly into the hub?
|
 PINPOINT TEST G: DRIVELINE VIBRATION - OCCURS AT CRUISING SPEEDS
PINPOINT TEST G: DRIVELINE VIBRATION - OCCURS AT CRUISING SPEEDS |
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions Halfshafts transmit rotary motion through constant velocity joints in a uniform manner. The outer CV joints use balls, have no length compensation and engage in the wheel hubs. The intermediate shaft (right side) is correctly positioned and secured in the differential by the intermediate shaft center bearing. The left CV joint is locked in the differential by a snap-ring. Possible Sources
|
||||
| G1 CHECK THE OUTER CONSTANT VELOCITY (CV) JOINT FOR CORRECT SEATING INTO THE HUB | ||||
Is the outer Constant Velocity (CV) joint seated correctly into the hub?
|
 Removal and Installation - Front Halfshaft LH
Removal and Installation - Front Halfshaft LH
Special Tool(s) /
General Equipment
204-161
(T97P-1175-A)
Installer, HalfshaftTKIT-1997-LM2TKIT-1997-F/FM2TKIT-1997-FLM2
205-D070
(D93P-1175-B)
Remover, Front Wheel Hub
Tie Rod End Remover
Removal
Remove the wheel and tire...
Other information:
Ford Escape 2020-2025 Service Manual: General Procedures - Spark Plug Inspection
Inspection NOTE: Dropped spark plugs should always be discarded. Unfired An unfired spark plug should appear very clean with a pure nickel finish to the threads and ground strap. The center electrode ceramic insulator surface is often a matte or dull finish and pure white in color...
Ford Escape 2020-2025 Service Manual: General Procedures - Heater Core Leak Check
Inspection NOTE: A coolant leak in the heater hose could follow the heater core tube to the heater core and appear as a leak in the heater core. Inspect for evidence of coolant leakage at the heater hose to heater core attachments. NOTE: Spring-type clamps are installed as original equipment...
Categories
- Manuals Home
- 4th Generation Ford Escape Owners Manual
- 4th Generation Ford Escape Service Manual
- Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle Drive Modes
- General Procedures - Brake Service Mode Activation and Deactivation
- Drive Modes
- New on site
- Most important about car
Under Hood Fuse Box
Locating the Under Hood Fuse Box
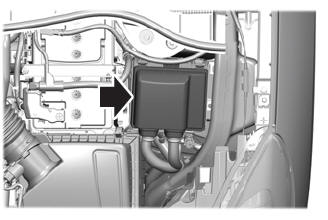
Accessing the Under Hood Fuse Box


 PINPOINT TEST A: AXLE HOWLING OR WHINE – FRONT OR REAR AXLE
PINPOINT TEST A: AXLE HOWLING OR WHINE – FRONT OR REAR AXLE 